Building & Construction Industry: Infrastructure: pipe market no more a pipe dream - August digital issue
Also, download this story from the electronic issue here
With increasing urbanisation, Southeast Asia is set to lead in infrastructure development. PricewaterhouseCoopers’s 2025 outlook on infrastructure spending cites that the Asian market will account for almost 60% of global infrastructure spending over the report period. The lucrative growth, especially in developing countries, will push demand for pipes and hoses. Global Industry Analyst (GIA) projects that the global market for pipes and pipe/hose fittings will be worth US$320 billion by 2020.
Pipes are of critical economic importance, forming the structural foundation of water, fuel and gas distribution such as hot water heating, air conditioning and refrigeration systems. Applications that require robustness of steel pipes are finding compatibility with plastic pipes, aided by technology advancements in manufacturing processes as well as material engineering.
GIA states that demand for plastic pipes is also expected to be driven by their growing use in the installation of marine and mining pipelines. In addition, the adoption of trenchless installation of pipelines offers lucrative opportunities for the growth of large diameter plastic pipes.
Securing clean water via plastic pipes
Access to safe water remains a challenge in Asia, where more than half the world’s population lives. Each person requires about 3,920 cu m of clean water/year. A report by the Asia Society Leadership Group estimates that more than a billion people or one out of six does not have access to safe water. The problem, if not addressed, will strike half the countries worldwide by 2025.
Given this plight for safe water, the importance of installing reliable infrastructure cannot be stressed enough. Persistence Market Research, in its study, explores the increasing use of plastic and competitive pipes for conveying potable water and wastewater.
Plastic pipes, of HDPE, ABS, CPVC and PVC, offer advantages over steel due to the ability to safeguard water quality. Steel is prone to corrosion and thus compromises water quality and reduces the pipe’s hydraulic capacity. Whereas, plastic pipes offer long service life, low breakage rates, flexibility and resistance to degradation, and thus translate to lower maintenance costs, according to the American Chemistry Council (ACC).
In the US, citing estimates of the Environment Protection Authority (EPA), ACC says that 3-4% of national electricity consumption, or approximately 56 billion kW, is spent for pumping drinking water and wastewater services each year. However, plastic pipes reduce propane use as well as emissions, materials, time and labour necessary to maintain traditional pipes.
Spanish firm Molecor, which specialises in the manufacture of PVC-O pipes for high pressure water conveying, has launched its 125 mm-diameter oriented-PVC (PVC-O) TOM pipe. The company developed the new pipe to provide an optimal technical and economical alternative for the design of hydraulic networks, and the development of new markets. The pipe is said to offer effective pressure strength under the required flow. “TOM pipes have the ability to intelligently manage the hydrological resources using new technology in the design of high-pressure water pipelines,” says the firm.

Molecor has already achieved an important milestone becoming the “worldwide pioneer” in the manufacturing of oriented-PVC pipe with diameters of 500, 630 and 800 mm, the company says.
The molecular orientation process provides the TOM pipe with improved mechanical and hydraulic characteristics compared with other materials used in existing pipelines. It also provides PVC-O pipes with significant advantages in the quality of the product, installation and use. TOM pipes also offer a smaller environmental footprint compared with other pipe materials, contributing to sustainability, says Molecor.
Green Building: challenge for safer pipes
Meanwhile, today’s billion-dollar infrastructure industry is more competitive than ever, with the trend shifting towards sustainable or green infrastructure. Research company Lucintel, in its analysis on the global plastic pipe market 2015- 2020, suggests that aside from infrastructure, the boom in residential and commercial construction will pave the way for market growth for plastic pipes through 2020. It points to Asia Pacific as the largest market over the report period.
Notwithstanding the benefits offered by plastic pipes, improvements are needed to ensure that water quality is preserved. US-based National Science Foundation has carried out a study and finds that several types of NSFI Standard 61-certified plastic pipes in green buildings in the US leach chemicals into drinking water that can cause odours and sometimes exist at levels that may exceed health standards. Also, some chemicals released by plumbing pipes are found to transform into carcinogens; while other leached chemicals encourage bacterial growth.
These green buildings use pipes made of crosslinked PE (PEX), HDPE, PVC, cPVC and PE for drinking water distribution because they are light, inexpensive, easy to install and have longer life cycles. Moreover, manufacturing plastic pipes uses less energy and thus produces less CO2 than making metal pipes, which make them befitting for green buildings. But the leaching of chemicals is a concern that is yet to be addressed by manufacturers and green building proponents.
The green building trend, thus, is prompting the industry to adopt eco-friendly pipes and hose fittings. The development of lead-free pipes can benefit the market, GIA reports, adding that ecofriendly friendly pipes could succeed demand for conventional PVC pipes.
New machinery for pipes

Germany-headquartered Unicor is known for its advanced corrugation technology and components and die heads for extruding corrugated pipes. Alongside its existing die heads, such as those for the production of wastewater and drainage pipes with diameters up to 1,800 mm, the company has released two new die heads for multi-layer manufacturing.
The SWP 58-2L is a modularly constructed die head designed for the manufacture of electrical conduits. Both single-layer and double-layer conduits can therefore be produced with PE/PP/PA and PVC/ABS materials. The TWP series, developed for the production of double wall corrugated pipes, particularly for underground use, allows the pipe manufacturer to use recycled granulates while maintaining the colour classification of the pipe types. To accomplish this, a new distribution system provides a symmetric pre-distribution, which in turn provides the thinnest cover layers and optimal colour coverage.
German-Austrian firm battenfeld-cincinnati, a technology leader in the portfolio of solutions for large diameter pipe extrusion, will introduce a newly-developed series of single-screw extruder, solEX NG for PO pipe lines with diameters of up to 2.6 m, at the upcoming K2016 show in Germany in October.
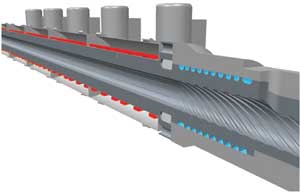
Developed on the basis of the solEX 40 D extruder series, this new generation features a new processing unit, with barrels, screws, and grooved bush completely redesigned. The major changes are an internally grooved barrel, a screw concept that consistently applies the theory of dispersive melting, as well as a feed zone with a completely revised geometry and fitted with spiral grooves. All three components are ideally matched, thus enabling a further improvement in the process. It is available in four sizes (60, 75, 90 and 120 mm) and offers outputs ranging from 1,000 to 2,500 kg/hour – an increase of up to 25% for each machine size compared to the original solEX series.
Benefits include an increase in melt capacity and a reduction in melt temperature in the extruder by up to 10°C for comparable outputs, while the melt homogeneity remains consistent.
The modification in the conveying mechanism reduces the axial pressure profile in the feed zone and the barrel, thus reducing pressure across the entire system and enabling an increase in output. In addition, higher amounts of regrind can be processed without impairing the process behaviour. Energy cost savings of up to 15% are possible since less drive energy is required and, secondly, due to the cooling of barrel and grooved bush significantly less heat discharge is necessary. As the basic structure of the extruder was retained from the previous series, existing solEX models can be retrofitted with the NG processing unit.
Meanwhile, also at K2016, German machine maker KraussMaffei Berstorff will showcase a custom solution for its 36D twin-screw extruder series, designed for extrusion of U-PVC pipes. By combining two KMD 108-36 E2/R twin-screw extruders, and the latest KM-RK 23-250 pipe head designed for large diameters with high output, with features such as flow channel volume and mandrel ridges for optimum flow, it will show the production of pipes at an output of up to 2,000 kg/hour. An advantage is that the space required is reduced by about one-third.
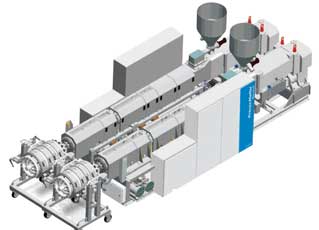
The main focus is on the long preheating length, which ensures a balanced combination of shearing energy and heating energy, optimal material processing and improved melt homogeneity - in addition to low compression values in the throttle zones. Optimal wear-resistance is guaranteed by the deep-nitrided barrels and the molybdenum welded layer on the screw threads, which allow higher-filled PVC compounds to be processed. Energy-savings are another benefit, lower compared to a larger extruder that uses the twinstrand, saving 0.02 kW per hour/kg of material throughput compared to a KMD 164-32/R.
Italian machine maker Amut has sold to a primary European pipe producer dedicated to hot and cold water ducting for civil and industrial applications a line able to produce pipes with diameter up to 630 mm for the production of multilayer-pipes in PP with glass fibre. The glass fibre improves the elastic module of the pipe, reducing the thermal expansion. Pipe installation costs are lower than the ones for traditional pipes because pipe support is reduced during installation.

The line is composed of three single screw-extruders, EA75 AMUT model, L/D 35:1, and one co-extruder EA20 for the coloured strips. The extruder for the inner layer is equipped with anti-abrasion treated screw and barrel to process the glass fibre. It also has a special head designed for processing large-sized pipes and different configurations: three-layer with spiral-helical distribution system. The head is thermoregulated through a dedicated TCU keeping accurate temperature during the production process (TERAX system). The pipe head is equipped with INRAF system for the internal cooling of the pipe. This energy saving concept allows the reduction of the number of cooling tanks, improving the dimensional quality of the pipe.
Manholes made of PP for sewerage systems
Ettlinger has supplied its 2,500-tonne 2500/120 injection moulding machine, with a maximum shot volume of 120 l, to a European processor to manufacture PP sewer manholes with a diameter of up to 1,000 mm. The modular manholes comprise an entrance cone, shaft ring, and shaft bottom, adding up to an overall height of several meters. The shaft bottom, which was moulded during the machine acceptance test, weighs 62 kg.
The newly commissioned SRM2500 is the second machine purchased by this client to expand its capacity for sewer manholes. The manufacturer of the PP sewer manholes was also swayed by several other points in the machine’s favour including the compact plasticisation unit and short clamping system that are combined in a single twin-platen machine, making an overall length that is 30% less than for a conventional machine with the same shot weight. At the same time, the tiebarless open space provides optimal accessibility from the side for removing moulded products or changing the mould. The manhole components are large and heavy, which is why an industrial robot is needed to remove them.

Sewer systems not only have to comply with extremely strict safety requirements; they must also be built to last. Compared to concrete – the material traditionally used to make manholes, PP is more resistant to aggressive media, both acid and alkali, as well as being non-corroding. Even hot sewage up to 60°C (or 90°C for short periods) is not a problem. At the same time, expert assessments have attested to a useful life of up to 100 years for PP sewer systems.
(PRA)Copyright (c) 2016 www.plasticsandrubberasia.com. All rights reserved.












































